5.3 Autosomal dominant inheritance
Preceding page
Factors indicating autosomal dominant inheritance.
- 1. Affected individuals occur in every generation
- 2. Affected offspring must have at least one affected parent
- 3. Normal offspring of affected parents get normal offspring
- 4. The population frequency is the same in males as in females
- 5. The segregation ratio is 1:1 among offspring of one normal and one affected
parent
Figure 5.3. 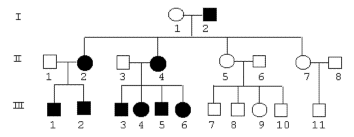
For examples of autosomal dominant inheritance, see Figure 5.3. Typical examples
of autosomal dominant inheritance
are genes coding for membrane proteins, building blocks in tissues etc.
Next page

